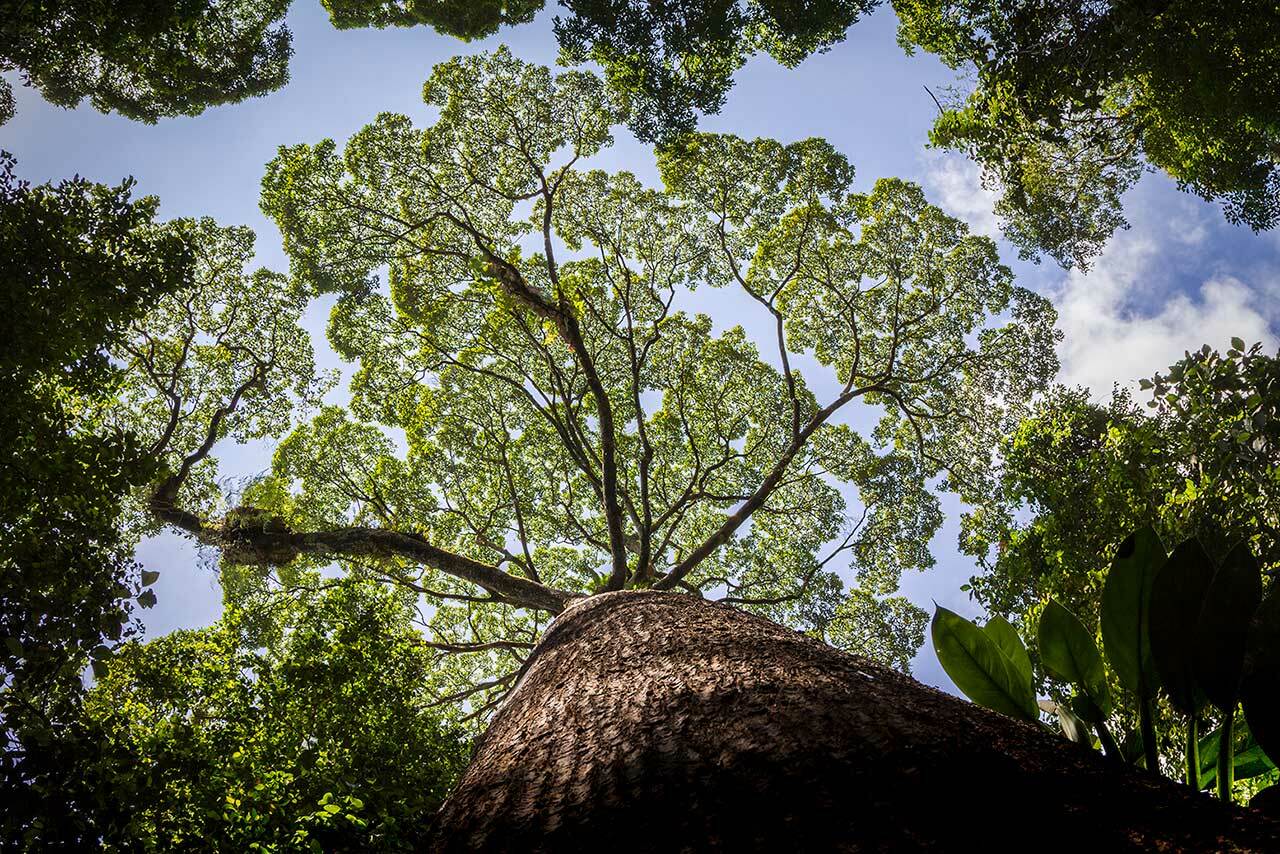
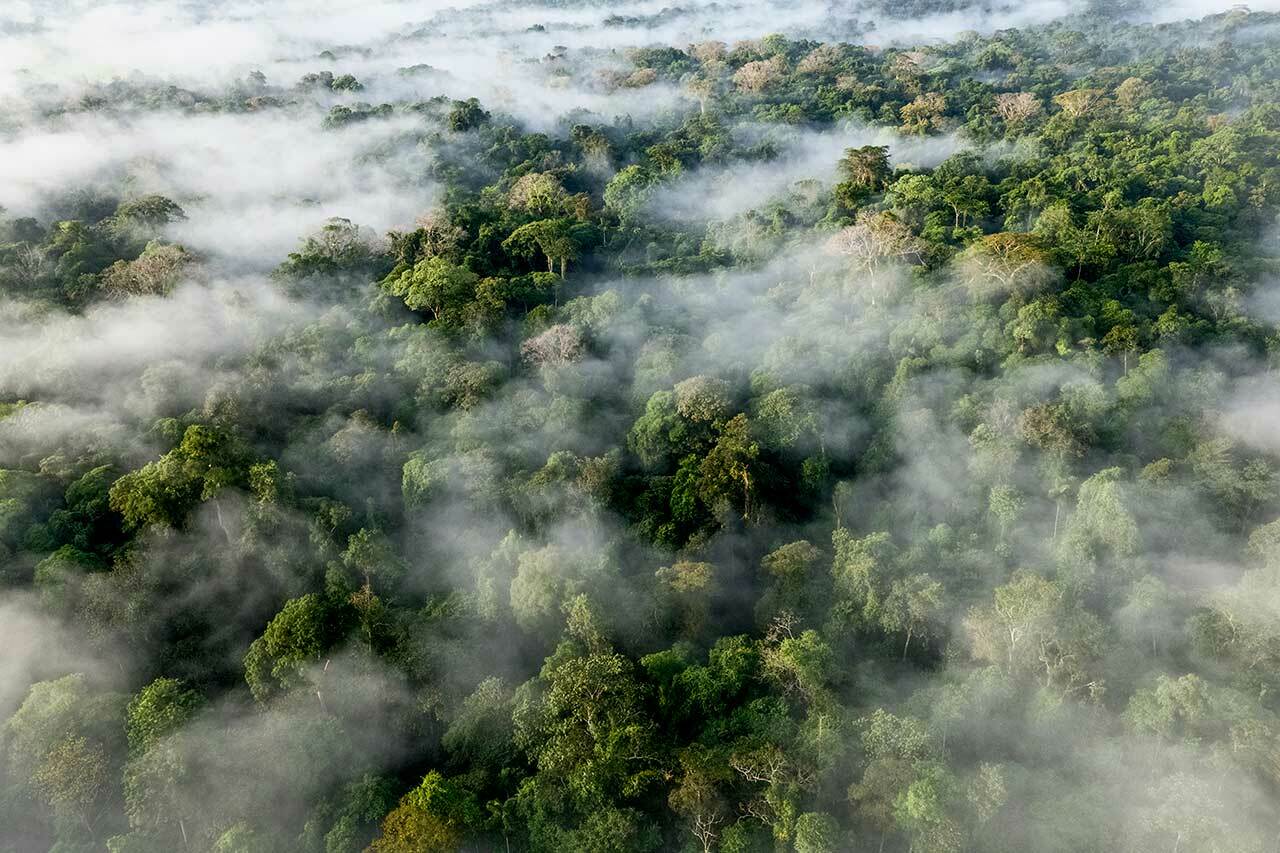
A tropical rainforest biome climate is an environment found near the Earth's equator, in locations such as South America, Africa, and Southeast Asia, characterized by high temperatures and high rainfall. The combination of these two factors creates a very humid environment that is perfect for plants and animals to thrive. As such, tropical rainforests are home to some of the most diverse ecosystems on the planet, and they are teeming with life. They are home to many types of plants, including trees, vines, and shrubs.
Some of the most popular rainforest flowers and plants, include palm trees, ferns, and orchids. The warm, moist conditions of the rainforest also make it an ideal environment for the growth of fungi and bacteria.
For all that live in the rainforest, some adaptation is required to the conditions. That is all the more true with regards to flora and fauna. With so many different types of plants, animals and insects living in the rainforest, we will look at how a few of them have adapted to their unique environment.
Leafcutter Ants

Leafcutter ants are a species of fungus-growing ant that is found in the tropical and subtropical regions of South and Central America. Considered to be one of the most sophisticated insect societies due to their complex social structure and their ability to engage in collective behavior, there are over 40 different species of leafcutter ant ranging in size from small to large. This sophistication can be seen in the behavior that gives these ants their name: leaf-cutting. Leafcutter ants use cut-up leaves to cultivate a special type of fungus that they eat. They do this by first cutting up leaves into small pieces before carrying them to their nest. Once at the nest, leafcutter ants will deposit the leaf pieces into a special chamber where they will be used to create a fungus garden. The fungus garden is an important part of the leaf cutter ant colony, as it provides food for the ants.
Leafcutter ants are also important members of the rainforest community. These hard-working insects help to keep the forest floor clear of dead leaves and other debris. This not only helps to maintain the health of the trees and other plants in the forest but also allows sunlight to reach the ground, which helps to prevent soil erosion. In addition, the leaf cutter ants’ composting activities help to fertilize the soil, which benefits all the plants in the forest. Without these ants, the leaves they carry would decompose and release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This would contribute to climate change, and it is thought that leaf cutter ants play a small but important role in helping to combat this problem.
Corpse Flower/ Rafflesia

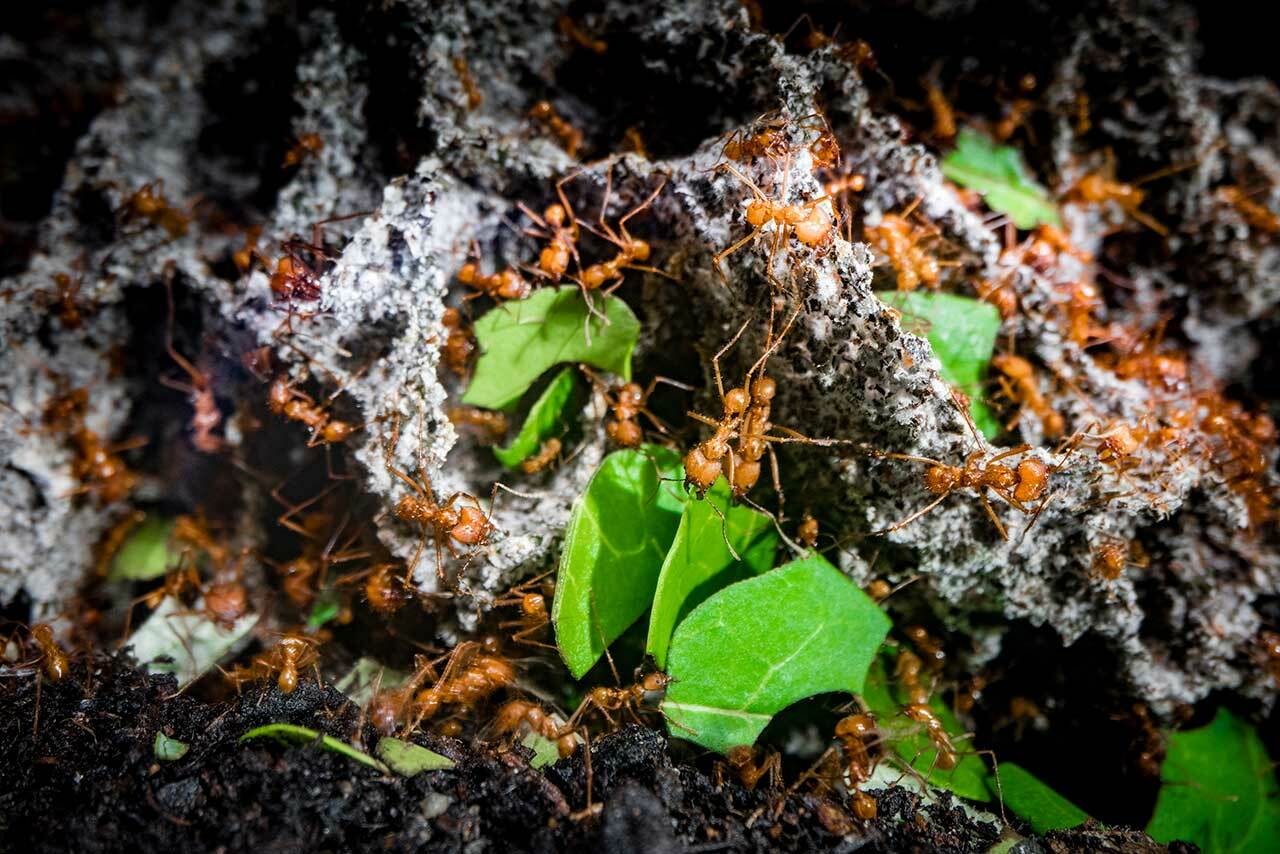
The corpse flower (rafflesia) is a unique plant that is found in the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia. This amazing plant gets its name from its ability to produce a large, foul-smelling bloom that smells like rotting flesh. This odor is thought to attract pollinators such as flies and carrion beetles, leading it to bloom. The blooms of the corpse flower can reach up to three feet in diameter and weigh up to 20 pounds! The corpse flower is also the largest flower in the world.
While the blooms of the corpse flower are impressive, it blooms very infrequently. It typically takes 7 to 10 years for the plant to bloom, and when it does, the blooms only last for a few days before they start to decompose. After the blooms die, the plants produce small, black fruits that are poisonous to humans.
Despite its gruesome appearance and smell, the corpse flower is a popular tourist attraction in Southeast Asia. Many people come to see the rare and amazing sight of this giant flower, one of the coolest flowers in bloom.
Balsa Tree

The balsa tree is a fast-growing tree that can reach up to 100 feet tall and can weigh up to 20 pounds. It is native to the tropical climates of South America, but it has been introduced to other parts of the world, such as Africa and Southeast Asia. The balsa tree is famous for its light, soft, and buoyant wood, which is harvested by cutting the tree down or by stripping a living tree of its bark. These unique features make balsa wood ideal for constructing rafts and other floating devices, as well as crafting, carving, and model-making. One common model balsa wood is used for is model airplanes. The wood is easy to work with and can be shaped into almost any form, making it perfect for creating intricate designs.
Balsa wood is also used in construction, packaging, model making, and crafts. For example, balsa wood is also often used in the construction of bridges. The wood's light weight makes it ideal for spanning large distances, while its strength ensures that the bridge will be able to support a heavy load. Balsa wood is also sometimes used to create sheets or other thin pieces of wood. Balsa trees are harvested for their wood by cutting them down or by stripping the bark off of living trees. The unique attributes of the wood of the balsa tree make it perfect for an incredible variety of applications.
Bioluminescent Fungus / Ghost Fungus
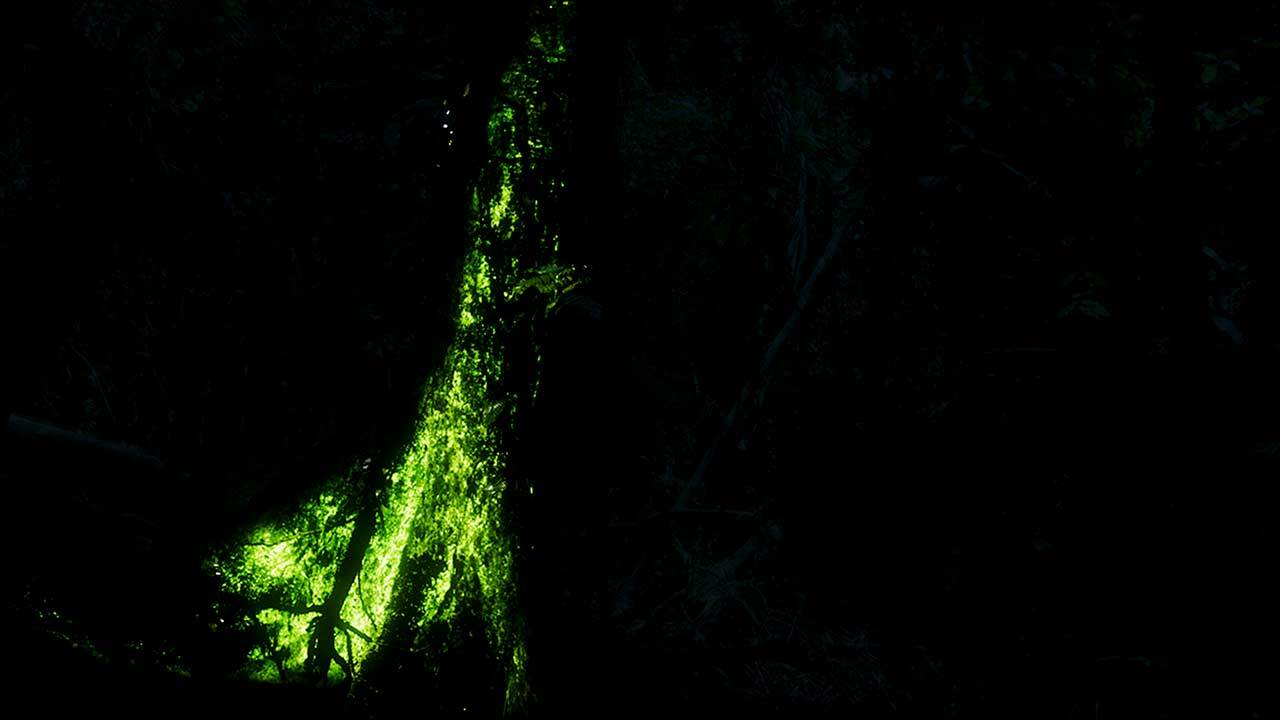

The bioluminescent fungus, also known as the ghost fungus, is a rare fungus found in dark, damp environments such as caves and forests. Most active at night, this strange creature emits a faint light from its body. This light is thought to help the fungus attract mates or deter predators by warning them of its poisonous nature. It also provides the fungus antioxidant protection, keeping it healthy. This eerie light is created by a chemical reaction between enzymes and luciferin, a compound found in the fungi's cells. When these two substances mix, they produce light. This process is similar to the one that causes fireflies to glow.
Bioluminescent fungi are relatively rare, but they can be found in some parts of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. Now while there is no evidence to suggest they are poisonous, if you are lucky enough to find one, it is important to avoid touching it or inhaling its spores, as they can cause allergic reactions in some people. If you do come into contact with the fungus, be sure to wash your hands and clothes thoroughly afterward.
While little is known about this strange creature, scientists believe that the bioluminescent fungus may be related to other fungi that emit light, such as glow-in-the-dark mushrooms. This fascinating creature is sure to continue to mystify and delight us for years to come!
Support your local PBS station in our mission to inspire, enrich, and educate.
Lianas / Drip Tips
Lianas, also known as drip tips, are a type of climbing plant that typically grows in tropical rainforests. They are characterized by their long winding and aerial roots that allow them to climb trees in the rainforest. In fact, lianas can reach lengths of up to 330 feet (100 meters), making them some of the longest plants in the world. In order to live in the rainforest, lianas have adapted by developing strong, flexible roots that can anchor themselves to tree trunks and branches. The roots of lianas also help to support the plant as it grows up into the canopy.
Lianas can be either woody or herbaceous, and they play an important role in the ecology of tropical rainforests by providing support for other plants and animals. Specifically, lianas are an important food source for many animals, including monkeys, sloths, and birds. They are also used by humans for construction purposes and as a source of fuelwood and timber. In some cases, lianas can actually be harmful to the forest ecosystem, particularly when they invade areas where they are not native.

The rainforest is one of the most important ecosystems on Earth. It is home to an incredible diversity of plant and animal species, many of which are still undiscovered. This ecosystem plays a vital role in regulating the global climate and supporting the Earth's biodiversity. It is, however, also a unique and extreme climate, with incredibly high temperatures and levels of rainfall. The dense vegetation and high humidity levels caused by this create a microclimate that is very different from other ecosystems. This means that plants and animals must adapt in order to survive in the rainforest. And throughout the eons, myriad plants and animals, including some features in this article, have done just that. This has allowed the rainforest to continue fulfilling its crucial role in the ecosystem. However, this adaptation may not be done. As the environment continues to change due to climate change and global warming, it is important that plants and animals continue to adapt with it.
This article was researched and compiled by Sandler Digital in collaboration with PBS.