If you’re like me, you’ve had a long withstanding date with the couch on Sunday nights to watch HBO’s breakout show The Last of Us. The show is about how the human population fights to survive a zombie apocalypse caused by a cordyceps fungus that spreads to the brain. The concept itself is scary enough, but many viewers are more startled by the fact that cordyceps fungi is very real.
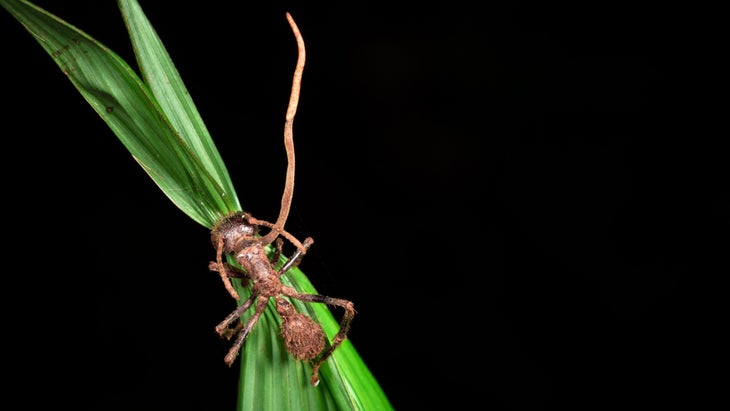
Cordyceps is a parasitic fungus that infects and sprouts through insect bodies. That’s right. Through insects – most commonly ants. If you’re brave enough to watch a sped up video of the processes, it’s both fascinating and jarring. The fungus is smart, targeting ants because they can be easily manipulated and taken over like, dare we say it, zombies. The infection takes control of the ant’s body and makes it climb to higher ground so that when a spore grows and releases particles, it’s more likely to infect other ants below.
Can Cordyceps Take Over Human Brains?
As realistic as the pandemic in The Last of Us is (thanks for the anxiety, Hollywood) there is no evidence that cordyceps fungus can infect humans. Thomas Russo, M.D. and chief of infectious disease at the University at Buffalo in New York, watches the show on Sunday nights and is more entertained than concerned.
“I can say with a high degree of certainty there’s zero concern for the human race as of now,” Russo says.
Russo explains that there are five million genus of fungal species and a limited number of them infect humans. “Compared to the magnitude of fungi we live with in the world, we live relatively copacetically with them,” he says.
Cordyceps, Russo says, are not a well-studied fungus. But there’s enough evidence that suggests, though not proven, that ants have a receptor that makes them susceptible that humans do not.
This fungus isn’t something to fear. In fact, it’s been touted as a delicious, nutritious snack for centuries.

Nutritional Benefits of Cordyceps Mushrooms
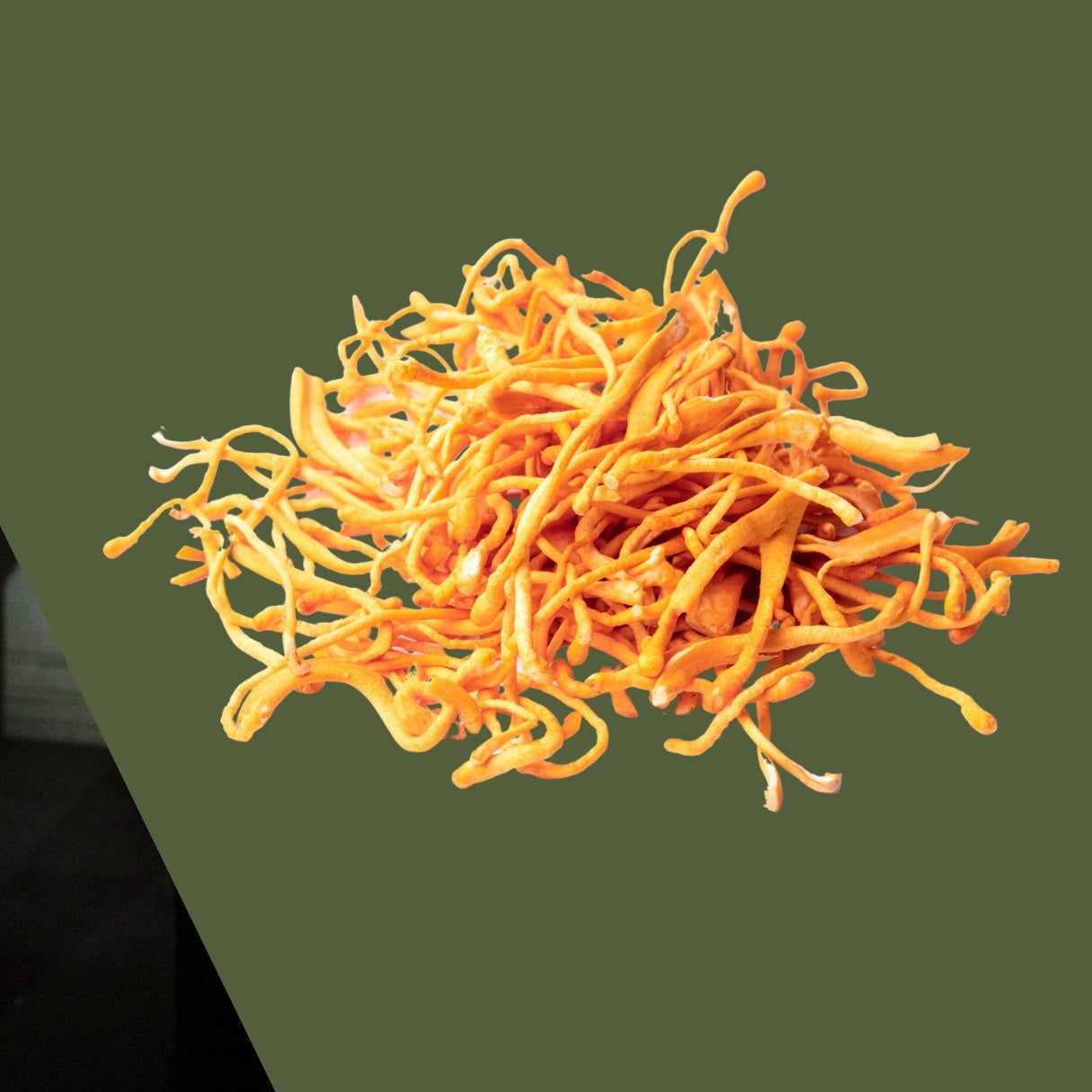
When harvested, Cordyceps resemble skinny Cheetos. Though most often seen in Southeast Asia, the fungus strain can be found in the U.S. growing on ants entombed on lower branches of beech trees. Cordyceps have a savory earthy flavor with a hint of nuttiness, similar to chestnut mushrooms. However they are rare, which is why fungi enthusiasts like Gretchen Testa (@mushroommusketeer on Instagram) cultivates her own.
“As growers, we have been able to engineer a substrate that mimics and even improves upon the insect it likes to grow on,” Testa says. “This is one type of fungus that grows much better in cultivation than it does in the wild.”She adds that cordyceps require 12 hours of daily light, 60-70°Fahrenheit and brown rice supplementation.
The fungus is not only not zombie-spawning, it’s actually been found to support kidney function due to its immunostimulant and antioxidant properties. In one large-scale study, cordyceps lowered creatinine levels in people with chronic kidney disease and helped protect kidneys from toxic drugs and diabetes complications. The fungus is also proven to reduce regulating levels of metabolic dysfunction to support heart health. It can lower levels of triglycerides and bad cholesterol, which prevents heart arrhythmias.
Perhaps most interesting to endurance athletes, cordyceps may boost athletic performance by improving stamina. One study found that participants who ate cordyceps improved their VO2 max – the maximum heart rate of oxygen consumption attainable during exercise – by as much as 10%. Additionally, the fungus increases production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), an energy pathway that supplies about 8-10 seconds of energy for intense, shorter running bursts.
How to Eat Cordyceps
Like any fungi, cordyceps can be eaten in a variety of ways. Testa prefers it in chicken noodle soup.“It’s also fabulous sautéed in butter, salt and pepper and then put on sandwiches,” she says. “The mushroom is mild tasting and takes the flavor of almost anything it’s cooked with. The texture is the thing I love most about them – it’s a pop on the teeth and a super soft center that is quite addicting.”
Testa showed us how to make the most satisfyingly crunchy cordyceps BLT, a perfect snack for the next airing of The Last of Us or after a tough endurance workout.