3 Major Ports of Angola
Located on the west coast of South Africa, Angola is the largest Portuguese speaking country only after Brazil.
Historically, the Portuguese settlers had a significant role in setting up the colony and subsequently influencing the economy and social structure of the country.
Angola shares its borders with the Democratic Republic of Congo in the North, Namibia in the South and Zambia in the East. Western Angola is a nearly 1600-km long coast along the South Atlantic Ocean.
The coastal plains are sparsely cultivated and populated, and house some of the most important coastal towns and ports of the country.
Initial Portuguese settlers started colonising the coastal areas in the early 16th Century and later on moved inland till most of the land was colonised by the late 19th Century.
After achieving independence from colonial rule in the year 1975, the country was torn by a civil war between three groups supported by different parties for control over the coastal country.
It wasn’t until 2002 that the country emerged as a stable state with the Marxist-Leninist One Party Republic taking over the governance.
Being endowed with bountiful mineral and petroleum reserves, Angola has always been the centre of international trade and conflict over the years, post-2002.
With major stakeholders of the economy coming from the United States and China, the wealth generation and wealth accumulation are highly uneven among the native population of the country.
High infant mortality rates and extremely poor standard of living in some of the regions is major causes of concern for the government of Angola. The 25 years of civil war had adversely impacted the infrastructure of the country, and it is still under development even after almost 20 years of stabilisation.
China is the biggest trade partner of Angola, besides United States and Brazil. Angola is a member of OPEC which is a confederation of 14 petroleum exporting countries of the world. It is also a founding member of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries which is an international co-operation among nations where Portuguese is the official language.
The community focuses on trade and development in the Lusophone Commonwealth Nations. Angola is also a member of the Southern African Development Community (SADC). The main aim of the organisation is to boost socio-economic relations among the member nations in the region.
Agriculture is the mainstay of Angolan economy, although it is one of the largest producers and exporters of petroleum and related products. Besides oil, Angola is highly dependent on mining and the export of diamonds as well. Since 2002, small plantations and farms have started sprouting in a scattered, unorganised manner as most of the infrastructure was destroyed in the civil war.
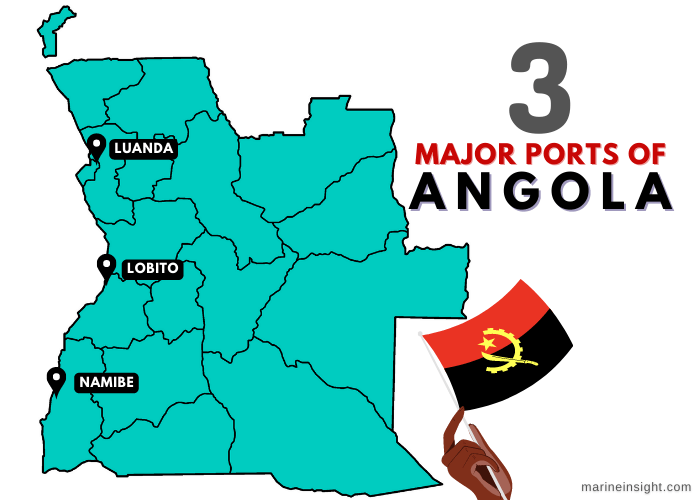
Angola has 5 major ports on the South Atlantic Ocean, facilitating international trade and tourism for the country. Let’s take a look at these ports in detail:
Port of Luanda: AOLAD
The Port of Luanda is one of the largest deep-water sea ports of Angola. The port city of Luanda is the capital of Angola and is also one of the largest commercial centres of the country. The Port of Luanda is being continuously developed to improve the infrastructure to facilitate international trade. Major goods exchanged through the port include automobile parts, beverages, and various agricultural products (cash crops) such as coffee, cotton, oilseeds etc.
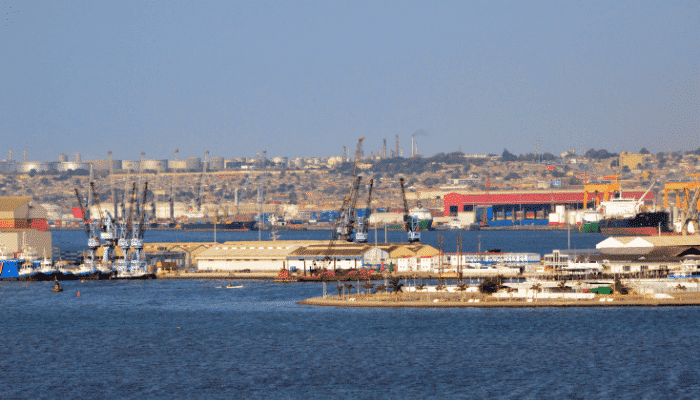

The port city houses an oil refinery as well, in the north of the Luanda Bay. The port of Luanda has an excellent natural harbour which allowed settlers to make land in and around as early as the 15th Century. The major contribution of the Portuguese settlers was setting up a freshwater supply channel which promoted the growth of the city. Today, the city is crowded with population displaced due to the civil war and the pressure on the basic amenities increases by the day.
Oil exploration and extraction remain the most important commercial activity of the country. The industries sprawling around the harbour transformed this region into one of the busiest commercial hubs. Petrochemicals, allied petroleum products, diamonds, seafood and iron ore are some of the most important and most produced materials in this region. Major imports include coal, grains, flour, steel, industrial and agricultural machinery, and automobiles.
The port has a maximum channel depth of 27.5 metres which goes down to 9.5 metres as one moves inwards. The quay side-draft is 23 metres on average which allows for bulk container ships to pass easily. The whole port is divided into 8 terminals, with one passenger terminal included. There is no storage or warehouse facility as of now, and the goods loading and unloading are done directly from carrier vehicles. Discharge rates reach 7000 MT daily directly from and to the trucks.
Port of Namibe: AOMSZ
The Port of Namibe is a small natural harbour that was originally used for fishing, and later expanded for handling complex cargo. The port is managed and operated by Empresa Portuaria do Namibe. The port is strategically important for serving the southern economic zone of Angola. It also functions as a transit port for the supply of goods inland to the far southeast of Angola. By cargo movement (loading, unloading and transhipment), the Port of Namibe is the third-largest port of the country.
Fishing and sea-food processing are the two main commercial activities in the region. Granite stone export is also one of the most important commercial activity carried out through the Port of Namibe. The nearest town is Mocamedes, and the port is connected to the rest of southern Angola through the Mocademes railway line.
The port has a maximum channel depth of 10.5 metres, and has total three zones for fishing, international vessels and passenger vessels respectively. The three piers can accommodate vessels worth 275m, 480m and 130m respectively, with a draft range of 3m to 10.5m throughout the length of the berth. An additional oil terminal has been developed with a draft of 19m and a berth length of 550m.
The port handling equipment include 3 dockside cranes of capacities from 5 to 15 MT, and 5 tug masters for navigation in the channel. Along with it, container facilities for accommodating 20ft and 40ft containers are also available on the port.
Port of Lobito: AOLOB
The Port of Lobito is the largest deep-water seaport of Central Angola. It is operated and managed by the Empresa Portuaria do Lobito which is a state enterprise for managing the development and day to day activities of the port. The agency takes support from various private companies for staffing, maintenance and carrying out daily business of the port operations.
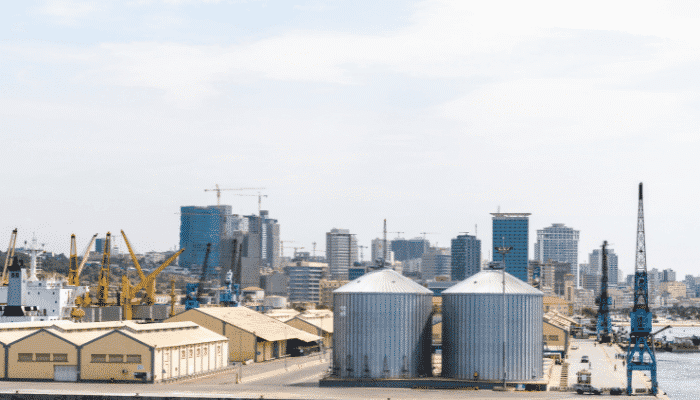

The city of Lobito is located in the Benguela province, which is connected to the commercial centre of Canata. The port has been one of the busiest ports of the country for several decades, but owing to the civil war, the railway lines and other infrastructure were severely damaged leaving the port void of any commercial activity for many years. The early 19th Century Benguela railway connected Lobito directly with DR Congo, and the conflict resulted in heavy losses to the network.
In recent times, connectivity is being improved to bring back the traffic of container goods and trans-shipment of goods from DR Congo and Zambia. This port, thus, not only serves as a strategic location for central Angola, but is also key to boosting trade for Central African nations that do not have direct access to the Atlantic Ocean. The city of Lobito and Canata combined have many small and large industries, manufacturing plants and shipyards for producing products such as small ships, processed sea-food, building materials, sugarcane products, metals etc.
The most striking feature of the Port of Lobito is the 5km sandspit that provides excellent protection to the natural harbour of the bay of Lobito. The port currently handles more than 2 million tonnes of cargo annually, which makes it the 2nd largest port (by container traffic) of Angola.
Recent Developments
The country is facing serious crisis of essential goods in recent years owing to the aftermath of Covid-19 pandemic that left international trade in doldrums. The Angolan government is doing its best to keep up with the demand for essential goods and services by trying to improve the logistic infrastructure of the country.
The port of Luanda which has been the top priority for the Angolan government, is set to receive an investment of close to USD 600 million from foreign entities that will carry out development and expansion work at the port.
This comes at a time when the Angolan economy is dwindling and needs support from a number of international agencies to keep the economy afloat. It is to be noted that the UAE has decided to invest the amount to develop Barra de Donde region of the capital city of Luanda to develop a stockyard for oil, gas and lubricants.
Another highlight is the International Public Tender for the Concession of the Multipurpose Terminal of the Port of Luanda is coming to fruition as 5 major international firms have made it through to the final stages of the competition. The winner of the tender will operate the Port of Luanda for a period not less than 25 years and must have enough equity (worth not less than USD 25 million) to run the port for the aforesaid period.
Conclusion
Owing to its strategic location and abundance of oil and mineral wealth, Angola has emerged as a strong contender for leading the economic reformation of Central and South Africa.
Although the country is small in size and was deeply affected by the 20 years of strife, it has managed to leverage its maritime location to boost trade and improve foreign relations with a number of Western and Eastern Countries.
It is important to note that while most of the Angolan infrastructure is witnessing a fresh reformative start, it is an excellent opportunity for major enterprises throughout the world to reap benefits by investing in development projects in Angola, the primary focus being the sea-port infrastructure of this fast-growing African nation.
You might also like to read:
- 5 Major Ports In Japan
- 6 Major Ports in Ghana
- 5 Major Ports In Guatemala
- 9 Major Ports in Kenya
- 5 Major Ports In Sudan
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Disclaimer :
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Latest Maritime Knowledge Articles You Would Like:
Daily Maritime News, Straight To Your Inbox
Sign Up To Get Daily Newsletters
Join over 60k+ people who read our daily newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.















