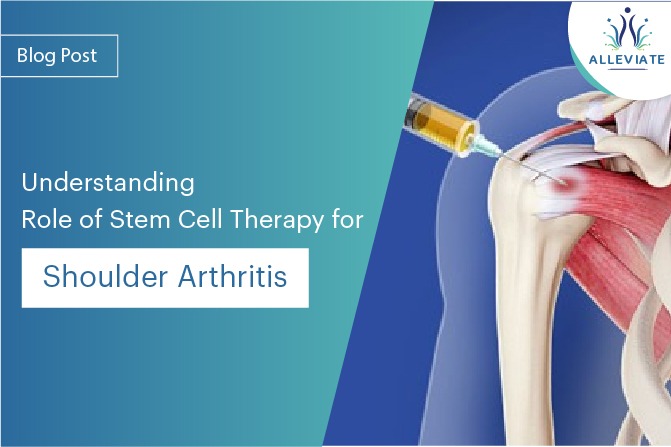
What is Stem Cell Treatment for Shoulder Arthritis, and How Does It Work?
Stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis is a regenerative therapy that harnesses the unique properties of stem cells to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation in the shoulder joint affected by arthritis. The goal of this treatment is to alleviate pain, improve joint function, and potentially slow down the progression of arthritis.
Understanding Stem Cells
Stem cells are unique cells in the body with the ability to transform into various cell types. They possess the remarkable capacity to differentiate into specialized cells, such as cartilage, bone, or tendon cells. In the context of shoulder arthritis, stem cells play a crucial role in regenerating damaged or degenerated tissues within the joint.
The Procedure
- Stem Cell Harvesting : The procedure begins with the collection of stem cells. These cells can be sourced from different places in the body, including bone marrow or adipose (fat) tissue. The choice of the source depends on factors like the patient’s medical history, the severity of arthritis, and the treating physician’s preferences.
- Processing and Concentration : Once harvested, the collected tissue is processed to isolate and concentrate the stem cells. In the case of bone marrow or fat-derived stem cells, the processing involves separating the stem cells from other components.
- Injection into the Shoulder Joint : The concentrated stem cells are then injected directly into the affected shoulder joint. This injection is usually guided by imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or fluoroscopy, to ensure precise placement of the stem cells within the arthritic joint.
Mechanism of Action
- Tissue Regeneration : Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into the specific cell types needed for tissue repair. In the context of shoulder arthritis, stem cells can transform into cartilage cells, promoting the regeneration of damaged cartilage within the joint.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects : Stem cells release anti-inflammatory proteins and growth factors that help modulate the local inflammatory environment in the shoulder joint. By reducing inflammation, stem cells contribute to pain relief and improved joint function.
- Stimulating Healing Cascade : Stem cells initiate a cascade of healing processes. They attract other cells involved in tissue repair and promote the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), enhancing the overall regenerative capacity of the treated area.
Expected Outcomes
Stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis aims to achieve several outcomes
- Pain Reduction : By promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation, stem cell therapy often leads to a significant reduction in joint pain associated with arthritis.
- Improved Joint Function : The regeneration of damaged tissues contributes to improved joint function, allowing individuals to regain mobility and perform daily activities with greater ease.
- Potential Disease Modification : While not a guaranteed outcome, there is evidence to suggest that stem cell therapy may have disease-modifying effects, slowing down the progression of arthritis in some cases.
Who is a Suitable Candidate for Stem Cell Therapy for Shoulder Arthritis?
Determining the suitability of an individual for stem cell therapy for shoulder arthritis involves a comprehensive assessment by healthcare professionals. While stem cell therapy holds promise for many, not everyone may be an ideal candidate. Several factors influence candidacy, and a thorough evaluation helps ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment. Here are key considerations for identifying suitable candidates
- Severity of Arthritis : Individuals with mild to moderate shoulder arthritis may be more suitable candidates for stem cell therapy. The extent of joint damage and the overall condition of the shoulder joint are important factors in the decision-making process.
- Failed Conservative Treatments : Suitable candidates often include individuals who have tried and failed to find relief through conservative treatments such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications. Stem cell therapy may be considered when conventional approaches have not provided adequate results.
- Overall Health and Medical History : A candidate’s overall health and medical history play a crucial role. Conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or active infections may impact the safety and effectiveness of stem cell therapy. A thorough review of medical records is essential.
- Age and General Fitness : While age alone is not a strict criterion, younger, generally healthy individuals may respond more favorably to stem cell therapy. Good overall fitness and a commitment to post-treatment rehabilitation contribute to the success of the procedure.
- Patient Expectations : Realistic expectations and understanding of the potential outcomes are important. Candidates should be aware that while stem cell therapy may provide pain relief and improve function, it may not guarantee a complete restoration of the joint, especially in cases of advanced arthritis.
- Imaging and Diagnostic Evaluations : Diagnostic imaging, such as MRI or X-rays, helps assess the extent of joint damage and guides the treatment plan. Healthcare professionals may use these images to identify suitable injection sites for precise delivery of stem cells into the affected areas.
- Commitment to Post-Treatment Care : Successful outcomes often hinge on post-treatment care, including rehabilitation exercises and lifestyle modifications. Candidates should be willing and able to follow through with recommended post-treatment care plans to optimize the benefits of stem cell therapy.
- Informed Consent : Informed consent is a critical aspect of candidacy. Candidates should have a clear understanding of the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes. Open communication with healthcare providers ensures that individuals make informed decisions about their treatment.
It’s crucial for individuals considering stem cell therapy for shoulder arthritis to consult with qualified healthcare professionals, including orthopedic specialists or regenerative medicine experts. These professionals can conduct a comprehensive evaluation, discuss treatment options, and determine whether stem cell therapy is a suitable and safe option based on the individual’s unique circumstances.
What types of stem cells are used in shoulder arthritis treatment?
Stem cells used in shoulder arthritis treatment can be sourced from various tissues within the body. Each type of stem cell has unique characteristics and potential applications in regenerative medicine. The choice of stem cell type depends on factors such as the patient’s medical history, the severity of arthritis, and the treating physician’s preferences. Here are common types of stem cells used in shoulder arthritis treatment:
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
- Source : Bone marrow, adipose (fat) tissue, synovial fluid.
- Characteristics : MSCs are multipotent cells capable of differentiating into various cell types, including chondrocytes (cartilage cells). They also exhibit anti-inflammatory properties.
- Application : MSCs are widely used in regenerative therapies for arthritis due to their ability to promote tissue repair and modulate the inflammatory environment.
Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs)
- Source : Adipose (fat) tissue.
- Characteristics : ADSCs are abundant in fat tissue and can differentiate into different cell lineages, including chondrocytes. They are often used in procedures involving liposuction to harvest the cells.
- Application : ADSCs are commonly employed in regenerative treatments for arthritis, including shoulder arthritis, to promote cartilage regeneration.
Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells
- Source : Bone marrow.
- Characteristics : Bone marrow is a rich source of hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells. Bone marrow-derived stem cells have the potential to differentiate into bone, cartilage, and other tissues.
- Application : Bone marrow-derived stem cells are frequently used in orthopedic regenerative therapies, including those targeting arthritis in the shoulder joint.
Synovial Fluid-Derived Stem Cells
- Source : Synovial fluid (fluid within the joint).
- Characteristics : Synovial fluid contains mesenchymal stem cells that contribute to joint homeostasis and repair. These cells can be isolated from the patient’s own synovial fluid.
- Application : Utilizing synovial fluid-derived stem cells is a less invasive approach, as it involves harvesting cells directly from the joint being treated.
Umbilical Cord-Derived Stem Cells
- Source : Umbilical cord tissue.
- Characteristics : Umbilical cord-derived stem cells are obtained from donated umbilical cords. They possess multipotent properties and are capable of differentiating into various cell types.
- Application : While less common in shoulder arthritis treatment, umbilical cord-derived stem cells have shown promise in regenerative medicine due to their regenerative potential.
Considerations
- Autologous vs. Allogeneic : Stem cells can be autologous (derived from the patient’s own body) or allogeneic (from a donor). Autologous cells are often preferred to minimize the risk of rejection or adverse reactions.
- Tissue-Specific Cells : The choice of stem cells may also consider their ability to differentiate into tissue-specific cell types, such as chondrocytes for cartilage repair.
- Regulatory Environment : The regulatory landscape may influence the availability and use of certain stem cell types. Clinicians adhere to established guidelines to ensure ethical and safe practices.
How is the stem cell injection administered for shoulder arthritis, and is it a painful procedure?
The administration of stem cell injections for shoulder arthritis is a carefully conducted medical procedure aimed at delivering regenerative cells to the affected joint. This process involves specific steps to ensure precision, safety, and optimal therapeutic outcomes.
Procedure Steps
- Patient Evaluation : Before the procedure, the patient undergoes a thorough evaluation, including a review of medical history, imaging studies (such as MRI or X-rays), and a physical examination. This evaluation helps determine the severity of arthritis, identify the injection site, and assess overall suitability for the treatment.
- Harvesting Stem Cells : Depending on the chosen source of stem cells (e.g., bone marrow, adipose tissue), a separate procedure may be conducted to harvest these cells. Harvesting methods can include bone marrow aspiration or liposuction for adipose-derived stem cells. In some cases, autologous stem cells may be collected from the patient’s own blood.
- Processing and Concentration : The harvested stem cells are processed and concentrated to create a solution rich in regenerative cells. This step often involves centrifugation or other separation techniques to isolate and enhance the concentration of stem cells.
- Imaging Guidance : To ensure precise delivery of stem cells to the affected area within the shoulder joint, imaging guidance is commonly employed. Techniques such as ultrasound or fluoroscopy allow the healthcare provider to visualize the joint in real-time, ensuring accurate placement of the injection.
- Local Anesthesia : Before the stem cell injection, the skin over the targeted area is typically numbed with a local anesthetic. This helps minimize discomfort during the injection procedure.
- Stem Cell Injection : Using a fine needle, the concentrated stem cell solution is injected directly into the identified site within the shoulder joint. The injection process is carefully controlled to optimize the distribution of stem cells within the affected area.
- Post-Injection Observation : After the injection, the patient is monitored for a short period to ensure there are no immediate adverse reactions. Most patients can resume normal activities relatively quickly, although specific post-injection instructions are provided.
Pain Perception and Management
The perception of pain during a stem cell injection for shoulder arthritis can vary among individuals. Factors influencing pain levels include the individual’s pain threshold, the use of local anesthesia, and the specific technique employed by the healthcare provider.
- Local Anesthesia : The application of local anesthesia to the injection site helps minimize pain and discomfort during the procedure.
- Discomfort vs. Pain : Patients commonly describe the procedure as causing mild discomfort rather than significant pain. The use of a thin needle and the relatively quick nature of the injection contribute to the overall tolerability.
- Post-Injection Pain : Some patients may experience mild soreness or discomfort at the injection site in the hours following the procedure. This is generally transient and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers as recommended by the healthcare provider.
- Patient Communication : Open communication between the patient and healthcare provider is crucial. Patients are encouraged to express any concerns or discomfort they may experience during the procedure.
What are the expected benefits and outcomes of stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis?
Stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis holds promise as a regenerative therapy that aims to address the underlying causes of arthritis, promote tissue repair, and alleviate symptoms. While individual responses may vary, there are several expected benefits and potential outcomes associated with stem cell therapy for shoulder arthritis
- Pain Reduction : One of the primary goals of stem cell treatment is to reduce pain associated with shoulder arthritis. Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties that can help modulate the local inflammatory environment within the joint, contributing to pain relief.
- Improved Joint Function : Stem cells have the potential to stimulate the regeneration of damaged tissues, including cartilage within the shoulder joint. As the joint structure improves, individuals may experience enhanced mobility and improved joint function.
- Tissue Regeneration : Stem cells can differentiate into various cell types, including chondrocytes (cartilage cells). By promoting the regeneration of damaged or degenerated cartilage, stem cell therapy aims to restore the structural integrity of the shoulder joint.
- Potential Disease Modification : While not guaranteed, there is evidence to suggest that stem cell therapy may have disease-modifying effects. By addressing the underlying causes of arthritis and promoting tissue regeneration, stem cells may contribute to slowing down the progression of the disease.
- Minimally Invasive Approach : Stem cell therapy offers a minimally invasive alternative to traditional surgical interventions. The procedure typically involves injections guided by imaging techniques, reducing the need for extensive incisions and potentially accelerating recovery.
- Autologous Cells : In many cases, stem cells used for treatment are autologous, meaning they are derived from the patient’s own body. This reduces the risk of rejection or adverse reactions and enhances the safety profile of the treatment.
- Reduced Reliance on Medications : For some individuals, successful stem cell therapy may lead to a reduction in the need for pain medications or anti-inflammatory drugs. This can positively impact overall well-being and reduce potential side effects associated with long-term medication use.
- Enhanced Quality of Life : By addressing pain, improving joint function, and promoting tissue regeneration, stem cell therapy has the potential to enhance the overall quality of life for individuals living with shoulder arthritis. This may include an increased ability to perform daily activities and participate in recreational pursuits.
- Patient Satisfaction : Positive outcomes and improvements in symptoms contribute to high levels of patient satisfaction with stem cell therapy. Many individuals report increased satisfaction with the treatment compared to traditional approaches.
- Long-Term Benefits : While the longevity of benefits may vary, some individuals experience sustained improvements in pain relief and joint function over the long term. Regular follow-up assessments help monitor and optimize the outcomes of stem cell therapy.
It’s important to note that while these expected benefits are reported in various studies and clinical experiences, individual responses to stem cell treatment can vary. The success of the therapy may depend on factors such as the severity of arthritis, overall health, and adherence to post-treatment recommendations. Individuals considering stem cell therapy for shoulder arthritis should consult with qualified healthcare professionals for personalized information based on their specific medical history and condition.
Are there any risks or potential side effects associated with stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis?
Risks and Potential Side Effects
Stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis is generally considered safe, especially when autologous cells (derived from the patient’s own body) are used. However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and side effects to be aware of:
- Infection : While rare, there is a risk of infection at the injection site.
- Bleeding or Bruising : Some individuals may experience minor bleeding or bruising at the site of stem cell injection.
- Allergic Reaction : Although rare, an allergic reaction to anesthesia or other components used during the procedure is possible.
It’s crucial for individuals considering stem cell therapy to discuss their medical history with healthcare providers to assess and minimize potential risks.
How long does it take to see results after undergoing stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis?
The timeline for experiencing results after stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis can vary among individuals. Some may notice improvements within a few weeks, while others may take several months to experience the full benefits. Patience is key, as the regenerative process and tissue repair initiated by stem cells can take time.
Is stem cell treatment a one-time procedure, or are multiple sessions required?
The number of sessions required for stem cell treatment depends on factors such as the severity of arthritis, the chosen source of stem cells, and individual response. While some individuals may benefit from a single session, others may require multiple sessions to achieve optimal outcomes. A comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals guides the determination of the appropriate treatment plan.
Can stem cell therapy be combined with other treatments for shoulder arthritis, such as physical therapy or medication?
Stem cell therapy can be complemented by other treatments to enhance overall outcomes for shoulder arthritis
- Physical Therapy : Combining stem cell treatment with physical therapy can optimize joint function and strengthen surrounding muscles.
- Medication : Stem cell therapy can be used in conjunction with medications for pain management and inflammation, providing a multifaceted approach to symptom relief.
The combination of treatments is often personalized based on the individual’s specific condition and response to therapy.
Is stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis covered by insurance, and what are the associated costs?
As of now, stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis may not be covered by insurance because it is considered an elective and innovative procedure. Insurance providers typically cover established and conventional treatments. The costs associated with stem cell therapy vary widely and depend on factors such as the clinic, the type of stem cells used, and the number of sessions required.
It’s essential for individuals to inquire about costs, payment plans, and potential financial assistance options when considering stem cell therapy. Some clinics offer consultations to discuss financial aspects and provide transparency regarding associated costs.
Conclusion
while stem cell treatment for shoulder arthritis shows promise, individuals should make informed decisions after thorough discussions with healthcare providers. Understanding the potential risks, expected results, session requirements, combination possibilities, and financial considerations is crucial for a well-informed approach to regenerative therapy. If you are thinking of undergoing Stem Cell Treatment for chronic pain do contact us at ALLEVIATE PAIN CLINIC for consultation with one of our Experts and understanding more about this procedure.










Leave a reply