- India
- International
PM Modi mentions Katchatheevu: Why the tiny, uninhabited island remains a hot-button political issue in TN
Indira Gandhi ceased India’s claim over Katchatheevu in 1974. But politicians, across the aisle, in Tamil Nadu continue to clamour for its return.
 Fishermen from Rameswaram routinely cross the Katchatheevu island and consider the area their traditional fishing terrritories. (Wikimedia Commons)
Fishermen from Rameswaram routinely cross the Katchatheevu island and consider the area their traditional fishing terrritories. (Wikimedia Commons) Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in his speech in the Parliament during the No Confidence debate on August 10, mentioned the island of Katchatheevu.
Hitting out at Rahul Gandhi for his now expunged Bharat Mata remarks, PM Modi said it was the Indira Gandhi government which gave away Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka in 1974.
“Katchatheevu is an island between Tamil Nadu and Sri Lanka. Somebody gave it to another country. It happened under the leadership of Indira Gandhi,” he said. “Wasn’t that part of Maa Bharati there?” he quipped.
Today a part of Sri Lanka, Katchatheevu remains a hot-button political issue in Tamil Nadu, for politicians across the aisle.
Just recently, ahead of Sri Lankan President Ranil Wickremsinghe’s visit to New Delhi, Tamil Nadu Chief Minister MK Stalin wrote to PM Modi requesting him to retrieve the island.

“The transfer of Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka, by the Union government, without the state government’s consent, has deprived Tamil Nadu fishermen’s rights and adversely impacted their livelihoods,” Stalin’s letter said.
Where is the island of Katchatheevu?
Katchatheevu is a 285-acre uninhabited speck in the Palk Strait, between India and Sri Lanka. It is no more than 1.6 km in length and slightly over 300 m wide at its broadest point.
It lies northeast of Rameswaram, about 33 km from the Indian coast. It is about 62 km southwest of Jaffna, at the northern tip of Sri Lanka, and 24 km away from the inhabited Delft Island, belonging to Sri Lanka.
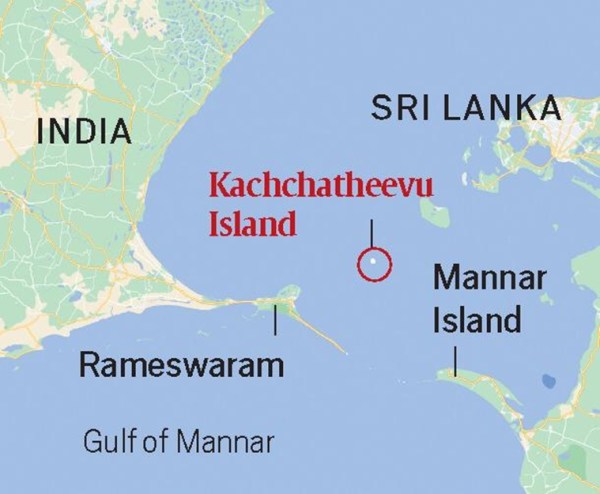 The tiny island of Katchatheevu lies 33 km northeast of Rameswaram and about 62 km southwest of Jaffna. (Express Image)
The tiny island of Katchatheevu lies 33 km northeast of Rameswaram and about 62 km southwest of Jaffna. (Express Image)
The only structure on the island is an early 20th century Catholic shrine – St Anthony’s church. During an annual festival, Christian priests from both India and Sri Lanka conduct the service, with devotees from both India and Sri Lanka making the pilgrimage. This year, 2,500 Indians made the journey to Katchatheevu from Rameswaram for the festival.
Katchatheevu is not suited for permanent settlement as there is no source of drinking water on the island.
What is the island’s history?
The island is relatively new in the geological timescale, being the product of a 14-century volcanic eruption.
In the early medieval period, it was controlled by the Jaffna kingdom of Sri Lanka. In the 17th century, control passed to the Ramnad zamindari based out of Ramanathapuram, about 55 km northwest of Rameswaram.
It became part of the Madras Presidency during the British Raj. But in 1921, both India and Sri Lanka, at the time British colonies, claimed Katchatheevu in order to determine fishing boundaries. A survey marked Katchatheevu in Sri Lanka, but a British delegation from India challenged this, citing ownership of the island by the Ramnad kingdom.
This dispute was not settled until 1974.
What is the agreement now?
In 1974, Indira Gandhi made attempts to settle the maritime border between India and Sri Lanka, once and for all.
As a part of this settlement, known as the ‘Indo-Sri Lankan Maritime agreement’, Indira Gandhi ‘ceded’ Katchatheevu to Sri Lanka. At the time, she thought the island had little strategic value and that ceasing India’s claim over the island would deepen its ties with its southern neighbour.
Moreover, as per the agreement, Indian fishermen were still allowed to access Katchatheevu “hitherto”. Unfortunately, the issue of fishing rights was not ironed out by the agreement. Sri Lanka interpreted Indian fishermens’ right to access Katchatheevu to be limited to “rest, drying nets and for visit to the Catholic shrine without visa”.
Another agreement in 1976, during the period of Emergency in India, barred either country from fishing in the other’s Exclusive Economic Zone. Again, Katchatheevu lay right at the edge of the EEZs of either country, retaining a degree of uncertainty with regards to fishing rights.
How did the Sri Lankan Civil War impact Katchatheevu?
However, between 1983 and 2009, the border dispute remained on the backburner as a bloody civil war raged in Sri Lanka.
With the Sri Lankan naval forces preoccupied in their task of cutting off supply lines of the LTTE based out of Jaffna, incursions by Indian fishermen well into Sri Lankan waters were commonplace. Bigger Indian trawlers were especially resented as they would not only tend to overfish but also damage Sri Lankan fishing nets and boats.
In 2009, the war with the LTTE ended, and things dramatically changed. Colombo beefed up its maritime defences, and turned focus to Indian fishermen. Facing a depletion of marine resources on the Indian side, they would frequently enter Sri Lankan waters as they had been doing for years, but finally began facing consequences.
Till date, the Sri Lankan navy routinely arrests Indian fishermen and there have been many allegations of custodial torture and death. The demand for Katchatheevu is revived each time such an incident happens.
What is Tamil Nadu’s position on Katchatheevu?
Katchatheevu was “given away” to Sri Lanka without consulting the Tamil Nadu state assembly. At the time itself, there were vehement protests against Indira Gandhi’s move, citing the historical control of the Ramnad zamindari over the island and traditional fishing rights of Indian Tamil fishermen.
In 1991, in the aftermath of India’s disastrous intervention in the Sri Lankan Civil War, the Tamil Nadu Assembly again sought retrieval of Katchatheevu and restoration of fishing rights of Tamil fishermen. Since then, Katchatheevu has perennially come up in Tamil politics.
In 2008, then AIADMK supremo, the late J Jayalalitha, filed a petition in court saying Katchatheevu could not be ceded to another country without a constitutional amendment. The petition argued the 1974 agreement had affected traditional fishing rights and livelihoods of Indian fishermen.
After becoming chief minister in 2011, she moved a resolution in the State Assembly and, in 2012, went to the Supreme Court asking her petition be expedited in the wake of increasing arrests of Indian fishermen by Sri Lanka.
However, the Union government’s position on Katchatheevu has largely remained unchanged. It has argued that since the island had always been under dispute, “no territory belonging to India was ceded nor sovereignty relinquished.”
While the BJP, especially the party’s Tamil Nadu unit, has been vocal in its demand for retrieving Katchatheevu for India, even the Narendra Modi government has done little to actually act on Tamil politicians’ demands – there is little it can do.
As then Attorney General Mukul Rohtagi had told the Supreme Court in 2014: “Katchatheevu went to Sri Lanka by an agreement in 1974… How can it be taken back today? If you want Katchatheevu back, you will have to go to war to get it back.”
More Explained
EXPRESS OPINION
Apr 28: Latest News
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05










































