- India
- International
Warming up to climate change: Is Earth becoming warmer?
In this series of explainers, we answer some of the most fundamental questions about climate change, the science behind it, and its impact. In the first instalment, we try to answer the question: 'Is the Earth becoming warmer?'
 One way to measure the Earth's warming is to observe the effects of rising temperatures. Oceans are getting warmer, snow and ice cover are depleting in the Northern Hemisphere, the Greenland ice sheet is shrinking, and the sea level is rising. (Via Pixabay)
One way to measure the Earth's warming is to observe the effects of rising temperatures. Oceans are getting warmer, snow and ice cover are depleting in the Northern Hemisphere, the Greenland ice sheet is shrinking, and the sea level is rising. (Via Pixabay)The 2023 summer was the hottest on record. Antarctic sea-ice extent reached a record low in the 45 years since satellite data was available. Arctic sea-ice extent remained well below normal. Extreme weather events ravaged all inhabited continents, exacerbating food insecurity, population displacement, and impacts on vulnerable people.
These are only a handful of the effects of climate change. Although scientists unequivocally agree that climate change is real, there are still many myths and a lot of confusion around the subject. In this series of explainers, we will try to answer some of the most fundamental questions about climate change, the science behind it, and its impact. In the first instalment, we try to answer the question: ‘Is the Earth becoming warmer?’
How do we know that the Earth is warming?
One way is to look at temperature measurements that in some cases extend to the late 1880s. Today, scientists use satellites to monitor surface temperature and put together, they indicate that the planet has become warmer. The average global temperature on Earth has increased by at least 1.1 degree Celsius since 1880, according to NASA.
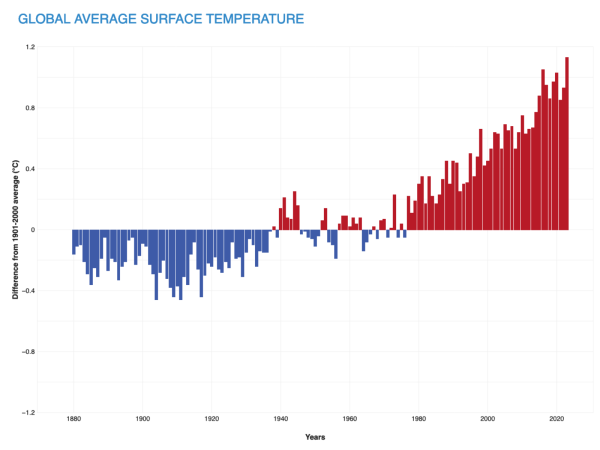 Yearly surface temperature compared to the 20th-century average from 1880–2022. Blue bars indicate cooler-than-average years; red bars show warmer-than-average years. NOAA Climate.gov graph, based on data from the National Centers for Environmental Information.
Yearly surface temperature compared to the 20th-century average from 1880–2022. Blue bars indicate cooler-than-average years; red bars show warmer-than-average years. NOAA Climate.gov graph, based on data from the National Centers for Environmental Information.
There are also indirect methods to verify the increasing temperature of Earth. A 1998 study that analysed tree rings, ice cores and other natural indicators, showed that temperatures remained fairly flat for centuries before turning sharply upward.
Another way is to observe the effects of rising temperatures. Oceans are getting warmer, snow and ice cover are depleting in the Northern Hemisphere, the Greenland ice sheet is shrinking, and the sea level is rising.

“These measurements are made with a variety of land-, ocean-, and space-based monitoring systems, which gives added confidence in the reality of global-scale warming of Earth’s climate,” according to ‘Climate Change: Evidence & Causes’, an analysis by the UK’s Royal Society and the US National Academy of Sciences.
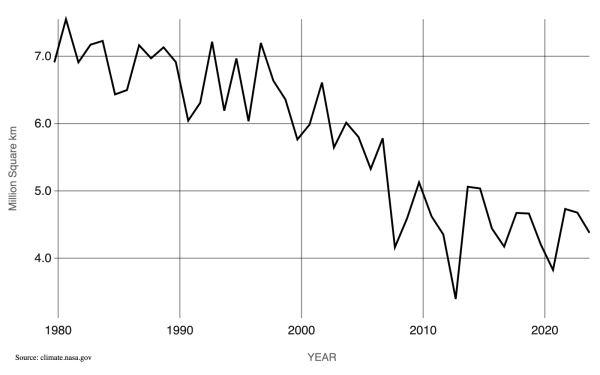 Arctic sea ice reaches its minimum extent each September. September Arctic sea ice is now shrinking at a rate of 12.2% per decade, compared to its average extent during the period from 1981 to 2010. This graph shows the size of the Arctic sea ice each September since satellite observations started in 1979. (Credit: NASA)
Arctic sea ice reaches its minimum extent each September. September Arctic sea ice is now shrinking at a rate of 12.2% per decade, compared to its average extent during the period from 1981 to 2010. This graph shows the size of the Arctic sea ice each September since satellite observations started in 1979. (Credit: NASA)
One can, however, argue that Earth’s climate has always changed in its 4.5 billion-year history. While this is true, the rapid warming taking place in recent decades can’t be attributed to natural cycles of cooling and warming.
“The kind of changes that would normally happen over hundreds of thousands of years are happening in decades,” a report by WWF said. For instance, the majority of the warming has occurred since 1975, at a rate of roughly 0.15 to 0.20 degree Celsius per decade.
Moreover, 2022 marked the 46th consecutive year (since 1977) with global temperatures rising above the 20th-century average. The 10-warmest years on record have all occurred since 2010, with the last nine years (2014-2022) among the 10-warmest years, a report by the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) said.
But what is behind Earth’s soaring temperature?
Simply put, greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Since the mid-19th Century, scientists have known that greenhouse gases have substantial control over Earth’s climate, despite their small amounts in the atmosphere. They trap the Sun’s energy in the Earth’s system before it escapes to space, leading to warming. This is known as the greenhouse effect, a process that is essential for keeping the planet at a suitable temperature for life.
The problem began when the Industrial Revolution kicked off in the 1700s. Human activities like the burning of fossil fuels like coal began to release high levels of greenhouse gases. As the global atmospheric concentrations of these gases went up, more and more heat got trapped and the Earth’s temperature started to increase.
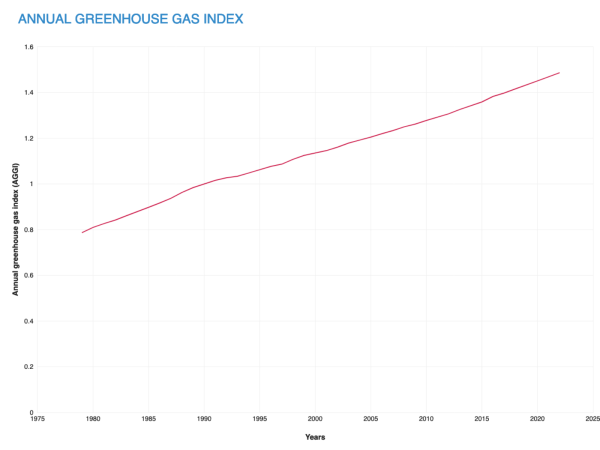 NOAA Climate.gov graph, based on data from NOAA Global Monitoring Lab.
NOAA Climate.gov graph, based on data from NOAA Global Monitoring Lab.
According to a March 2023 Synthesis Report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), “human activities, principally through greenhouse gas emissions, have unequivocally caused global warming. The main drivers of these emissions are energy use, land use, and the consumption and production of goods.”
More Explained
EXPRESS OPINION
May 06: Latest News
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05